This article is intended to provide general information about refusing a breathalyzer test and does not constitute legal advice. Always consult with a qualified attorney for advice specific to your situation and your jurisdiction’s laws.
Refusing a breathalyzer test when suspected of driving under the influence can result in serious legal implications. In most jurisdictions, such refusal could lead to license suspension, potential jail time, or even strengthen the prosecution’s case against you in court. The refusal could be used as evidence in a trial and DUI/DWI charges could be levied based on other evidences like officer observations or field sobriety test results. Additionally, some states differentiate between penalties for refusing a roadside Breathalyzer and post-arrest tests at a police station or hospital, the latter often carrying more severe consequences.
Refusing breathalyzer tests during traffic stops is a choice that comes with both potential rights and consequences. A breathalyzer test is a tool commonly used by law enforcement officers to determine if a driver is operating a vehicle under the influence of alcohol. However, the decision to refuse such a test is not one to be taken lightly. This article will delve into the implications, rights, and legal consequences of refusing breathalyzer tests.
Navigating the Consequences of Refusing a Breathalyzer Test

While it’s generally disadvantageous to refuse a breathalyzer test due to the serious repercussions it may entail, such as suspension of driving privileges, substantial fines, and potential incarceration, it’s essential to remember that this scenario isn’t a dead-end situation. If you ever find yourself having refused a breathalyzer test, there are several solutions and legal strategies available.
The most significant step is to engage the services of a proficient DUI attorney who can provide guidance through this complex process. They can help you comprehend your rights and might be able to contest the refusal charges or mitigate the severity of the consequences. Each case possesses unique characteristics, with varying outcomes depending on the distinct circumstances, which underscores the importance of seeking specialized legal counsel if you’ve refused a breathalyzer test.
Refusing a Breathalyzer Test: Possible Legal Defenses or Arguments
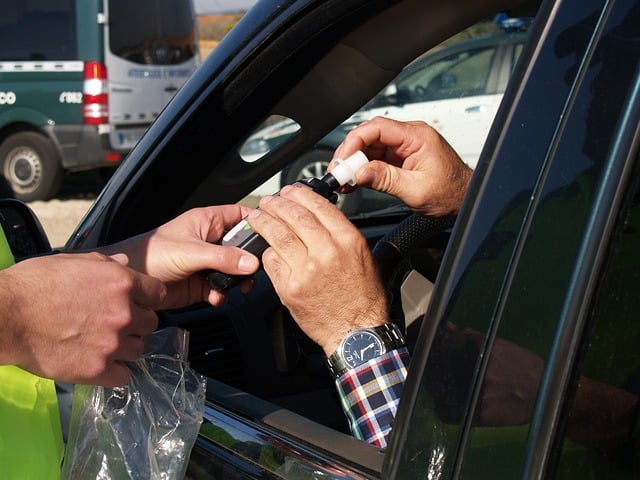

If you have refused a breathalyzer test, you might find yourself in a challenging legal situation. It’s crucial to speak with a qualified attorney who can guide you through the process and potentially help with your defense. Some possible legal defenses or arguments might include:
Invalid Stop
Your attorney may argue that there was no valid reason for the traffic stop in the first place, which might invalidate any subsequent actions, including a breathalyzer refusal.
Faulty Testing Equipment
If the breathalyzer was actually administered before the refusal, an attorney might argue that the equipment was faulty or not correctly calibrated, thus rendering the results unreliable.
Incorrect Administration of Test
Another argument could be that the police officer did not correctly administer the test or did not follow proper procedures, which could affect the validity of the test results.
Medical Reasons
Some people might have medical conditions that prevent them from providing a sufficient breath sample. This could potentially be used as a defense.
Lack of Proper Explanation
If the police officer did not adequately explain the consequences of refusing the breathalyzer test, this might be a possible defense.
Remember, these are general possible defenses and might not apply to your specific case. Always consult with a lawyer for advice tailored to your situation.
Understanding Breathalyzer Tests
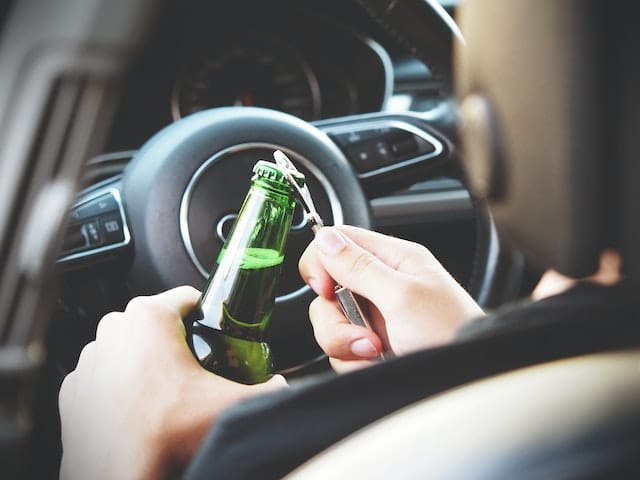

A breathalyzer is a device designed to measure the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) in an individual’s breath, providing an estimate of the amount of alcohol in their bloodstream. Police officers use breathalyzers during traffic stops when they suspect a driver is intoxicated. The results can serve as evidence in court cases related to Driving Under the Influence (DUI) or Driving While Intoxicated (DWI) charges.
Understanding the Difference Between DUI and DWI
Both DUI (Driving Under the Influence) and DWI (Driving While Intoxicated) refer to the illegal act of driving a vehicle while impaired by alcohol or other drugs, including prescription medications and illegal substances. While they are often used interchangeably, in some jurisdictions, they might refer to slightly different offenses.
DUI is typically used when a driver is charged with being under the influence of drugs or alcohol. It often refers to drivers who are found to be impaired through a field sobriety test or a breathalyzer showing any level of impairment or a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level over the state’s maximum limit, commonly 0.08% in many jurisdictions.
On the other hand, DWI, is usually used when a driver is charged with being intoxicated from alcohol. In many jurisdictions, this term is used when a driver is found to be impaired and their blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level is over the state’s maximum limit. In some states, DWI might also refer to driving while impaired by drugs other than alcohol.
However, the interpretation and application of these terms can vary from one jurisdiction to another. In some states, DWI is used for alcohol impairments, while DUI is used when the driver is charged with being under the influence of drugs. In yet other states, DUI is the more serious offense. The difference often comes down to the specific language of the law in each state or country. As such, it’s always a good idea to familiarize yourself with the laws in your specific area.
Moreover, regardless of the specific acronym used, DUI and DWI charges carry severe penalties, including fines, jail time, and the suspension of driving privileges.
Legal Rights Regarding Breathalyzer Tests
In many jurisdictions, driving is considered a privilege, not a right, and is subject to certain conditions. Among these is the “implied consent” law, which stipulates that drivers have implicitly agreed to submit to breathalyzer tests as a condition of their driving privileges. This law may vary slightly from state to state, but its overall aim remains the same: to deter drunk driving.
That said, drivers maintain the right to refuse a breathalyzer test, although this decision may carry significant legal consequences. It’s crucial to note that refusing a breathalyzer test does not guarantee an escape from legal charges. Law enforcement officers may use other evidence, such as field sobriety test results, erratic driving behavior, or physical signs of intoxication, to support a DUI/DWI charge.
Consequences of Refusing a Breathalyzer Test

Declining a breathalyzer test can result in significant repercussions, such as the suspension of your driving privileges, the possibility of incarceration, or an advantage for the prosecution in a DUI/DWI court case. Such repercussions may also involve being taken into custody if the police deem you as a threat, amplified fines and sanctions, and extended periods of imprisonment for those with prior offenses. In certain jurisdictions, the very act of refusing may be perceived as an acknowledgment of culpability.
In court, the refusal to take a breathalyzer test can be seen as an admission of guilt and may influence the proceedings against the accused. Moreover, a record of refusal can result in increased penalties in the event of future DUI/DWI charges.
The Role of Legal Counsel
If you’re faced with a DUI/DWI charge or have refused a breathalyzer test, it’s crucial to seek legal counsel as soon as possible. A knowledgeable attorney can help navigate the legal system, ensure your rights are upheld, and potentially mitigate the consequences you face.
Refusing Breathalyzer: Case Studies
The legal landscape is filled with cases where individuals have refused breathalyzer tests, with outcomes varying widely. These cases underscore the complex interplay between individual rights, legal obligations, and the pursuit of public safety. They serve as a stark reminder that refusing a breathalyzer is a decision with potentially significant legal repercussions.
New Florida Bill Proposes Increased Penalties for Breathalyzer Test Refusal: Ignition Interlocks on the Horizon
For example, in Florida, a proposed bill could impose harsher penalties on drivers who refuse breathalyzer tests. The legislation, introduced by State Representative Traci Koster, seeks to enforce Florida’s existing implied consent law and increase its penalties. Thomas Carey, a personal injury attorney and advocate for DUI victims, supports the bill, believing it can save lives.
Currently, under Florida law, drivers who refuse a breathalyzer test face a suspension of their license ranging from one year to 18 months. Koster’s bill proposes more severe consequences. For a first-time offense, in addition to the one-year suspension, offenders would be required to install an ignition interlock device in their frequently used vehicle, at their expense. The device requires a successful breath test before the car will start. Further refusals to take the breathalyzer test would extend the required use of the device to 18 months, also at the driver’s expense.
“Passive sample”: Arizona Officer’s Unconventional Breathalyzer Tactic Sparks Controversy
In a recent roadside DUI investigation in Gilbert, Arizona, Officer Andrew Templeton used an unusual strategy to gather evidence. After a driver refused a breathalyzer test, the officer asked the handcuffed individual to close his eyes and tilt his head back under the pretense of inspecting the driver’s eyes. Templeton then placed a breathalyzer in front of the driver’s face to capture a “passive sample” of his breath, detecting alcohol.
The incident, recorded on body camera video, has sparked controversy, with the driver’s defense attorney raising serious questions about the legality of Templeton’s tactics. While the Gilbert Police Department hasn’t explicitly forbidden this practice, critics argue that it encroaches on constitutional rights. The case is ongoing, with the court yet to rule on any potential constitutional violation.
Georgia Supreme Court Decision: Right to Refuse Breathalyzers, But Blood Tests Remain Viable
After the decision by the Georgia Supreme Court on February 18th, 2019, drivers in the state now have the right to reject breathalyzer tests without the risk of being arrested for their refusal. This refusal cannot be utilized as evidence against them in a court of law. However, other prosecutorial methods to charge impaired drivers are still in effect. While breathalyzer tests have been rendered optional, standardized field sobriety tests, along with body camera recordings, continue to form substantial evidence in DUI charges.
Despite refusal of the breath test, law enforcement officers can still secure a search warrant on the basis of probable cause to conduct a blood test. Even if drivers refuse the breathalyzer test, their behavior throughout the traffic stop, especially during field sobriety tests, can still lead to a DUI arrest. The Supreme Court’s decision has necessitated a revision of Georgia’s Implied Consent Law, which previously allowed a refusal of a breathalyzer test to be used against defendants. This new ruling applies solely to future DUI cases.
Ontario Motorist Avoids Impaired Driving Charge by Refusing Breathalyzer Test
An Ontario motorist, Matthew Durys, dodged a potentially severe penalty for impaired driving by refusing to provide a breath sample for an alcohol impairment test to a Greater Sudbury Police officer. Durys was originally charged with refusing a breath sample request, a charge that is similar to impaired driving and usually leads to harsh outcomes in court. However, he managed to plead to a lesser charge of obstructing a police officer, resulting in a one-year conditional discharge instead of a serious penalty.
The conditional discharge includes stipulations that Durys cannot drive with any alcohol in his system and must participate in the province’s Back on Track program. If he maintains a clean record for the next year, he will not have a criminal record. The outcome highlights a unique instance in which refusing a breath sample led to a less severe punishment.
Drunken Snowmobiling Incident in Wisconsin: Law Enforcement Officers Arrested, One Refuses Breathalyzer Test
Two law enforcement officers from Racine County, Wisconsin, Lt. Shawn Barker and Investigator Todd Lauer, were arrested on suspicion of operating snowmobiles while intoxicated. The arrests occurred on February 11, 2023 during an off-duty trip to Eagle River in northern Wisconsin. Barker refused a breathalyzer test, while Lauer was found to have a blood-alcohol content of 0.14, nearly twice the legal limit. Both officers are now facing non-criminal traffic citations for their alleged intoxicated snowmobiling in Vilas County. Their respective departments have initiated internal investigations into the incident.
Refusing Breathalyzer Test: FAQs
What happens if I refuse a breathalyzer test?
Refusing a breathalyzer test can lead to serious consequences, including license suspension, potential jail time, or strengthening the prosecution’s case in a DUI/DWI trial. Consequences can also include arrest if law enforcement believes you pose a danger, increased fines and penalties, and longer jail time for repeat offenders. In some jurisdictions, refusal itself can be seen as an admission of guilt.
Can my refusal to take a breathalyzer test be used against me in court?
In many jurisdictions, your refusal to take a breathalyzer test can indeed be used against you in court.
Are there different penalties for refusing a roadside Breathalyzer versus a post-arrest test?
Yes, some states distinguish between the penalties for refusing a roadside breathalyzer and those for refusing post-arrest tests at a police station or hospital, with the latter often carrying more severe consequences.
Can I still be charged with DUI/DWI even if I refuse a breathalyzer test?
Yes, prosecutors can still base a DUI/DWI charge on other evidence collected at the scene, such as officer observations or results of a field sobriety test.
What are implied consent laws?
Implied consent laws, which you agree to when obtaining your driver’s license, mean that you’ve agreed to submit to blood, urine, and/or breath tests when requested by law enforcement, perform field sobriety tests when asked, and carry a driver’s license and proof of insurance. Refusing a breathalyzer test would violate these laws and could lead to penalties even without a drunk driving conviction.
What are no-refusal policies?
No-refusal policies, adopted by some states, allow law enforcement to obtain immediate search warrants for blood samples to determine if a driver is under the influence. In some states, refusal to comply is considered an admission of guilt and may result in more severe penalties.
How does the implied consent law vary by state?
Regulations of implied consent laws can differ from state to state. It’s important to be aware of your state’s specific laws so you can make informed decisions.
What is the legal blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limit for driving?
In most states, it’s illegal to operate a vehicle with a BAC level over 0.08%. Anyone under the age of 21 is prohibited from driving with any level of alcohol in their blood in all states.
What is the Birchfield v. North Dakota Supreme Court decision?
The 2016 Supreme Court decision of Birchfield v. North Dakota states that people can refuse warrantless blood tests without criminal punishment since these tests can be considered invasive. However, refusal of a breath test can still result in penalties.


